WWII Era Cottage
1935 - 1950
 The WWII Era Cottage resembles the Workingman’s Foursquare of the proceeding decade but utilized the latest advancements in spatial planning and building materials. The type serves as a transitional form, bridging the gap between the Bungalow and Cottages of the 1920s to sprawling Ranch of the 1950s.
The WWII Era Cottage resembles the Workingman’s Foursquare of the proceeding decade but utilized the latest advancements in spatial planning and building materials. The type serves as a transitional form, bridging the gap between the Bungalow and Cottages of the 1920s to sprawling Ranch of the 1950s.
After WWII, with the peacetime economy just beginning to start up, materials were still in short supply. However the demand for housing was great, exacerbated by returning GI’s and their new families. As a response to the situation, new homes of modest designs, like the WWII Era Cottage were built in large quantities. Featuring little ornamentation, WWII Era Cottages are generally small (some less than 1,000 sq ft), and correspond to the small size needs of young families. Most were built by speculative builders and purchased by families who took advantage of a variety of government incentive programs which were offered through the Federal Housing Administration. Because of their simplicity and low cost, WWII Era Cottages made the dream of home ownership possible for an unprecedented number of people.
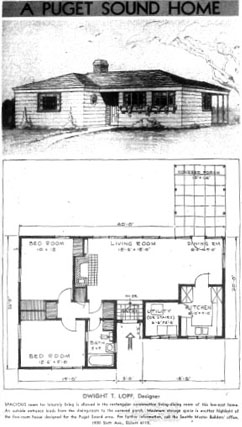 Sometimes referred to as “Roosevelt Cottages”, WWII Era Cottages are one-story structures covered by a hipped roof with minimal eave overhangs. The overall shape is typically square or rectangular in plan, although many boast more complex footprints that incorporate attached garages and shallow room projections. These projections can have hip or gable roofs. Large porches are generally absent; although a small covering or hood may be found over the front door, and/or a shallow stoop can be inserted into a projecting wing. The exteriors of these wood-framed buildings are sheathed with a wide range of materials from horizontal wood siding, wood shingles, stucco or brick, to asbestos ceramic shingles. Some concrete block and clay tile examples can be found. Higher end examples utilize a change in exterior material using the window sill as a breaking pointffor two contrasting sheating materials.
Sometimes referred to as “Roosevelt Cottages”, WWII Era Cottages are one-story structures covered by a hipped roof with minimal eave overhangs. The overall shape is typically square or rectangular in plan, although many boast more complex footprints that incorporate attached garages and shallow room projections. These projections can have hip or gable roofs. Large porches are generally absent; although a small covering or hood may be found over the front door, and/or a shallow stoop can be inserted into a projecting wing. The exteriors of these wood-framed buildings are sheathed with a wide range of materials from horizontal wood siding, wood shingles, stucco or brick, to asbestos ceramic shingles. Some concrete block and clay tile examples can be found. Higher end examples utilize a change in exterior material using the window sill as a breaking pointffor two contrasting sheating materials.
WWII Era Cottages have a noticeable absence of stylistic ornamentation, hence often refered to as Minimal Traditional in style. However, early examples often have Art Deco or Streamlined Moderne elements such as glass block and rounded porch features. Wide frieze boards and vertical siding in gable ends might add a playful detail. Towards the late 1940s, brick and stone became common as decorative accents, particularly in the form of water tables and raised flower planters. Many have a single octagonal window on the main façade near the front entry door. Other windows are tall and wide, many featuring just horizontal muntin bars. Often windows are placed at the corners of the house and wrap around two elevations.
Washington State Examples
 |
 |
 |
| Mary Mason House Aberdeen, c.1945 |
Apartments Pullman, 1948 |
House Seattle, c.1940 |
 |
 |
 |
| House Bremerton, c.1939 |
House Seattle, c.1945 |
House Auburn, c. 1947 |
 |
 |
 |
| House Longview, c.1946 |
House Monroe, c.1949 |
House Spokane, c.1953 |
For More Information:
- Helping Today's Home Builders Get their Money's Worth - Weyerhaeuser 4-Square - 1947
- Small Home Architectual Plan Book - Howard H. Riley, Seattle, WA. 1937.
- "Model Home in Modern" Pamphlet, 3rd Annual National Housing Exposition, Seattle, Febuary 1-9, 1941.
- Mid-Century Modern Architecture in Washington State: WWII Era Cottage - Michael Houser - June 2014
- "Small Homes Year Book" 1941 Show Edition.
- "A Puget Sound Home" Seattle Times, September 28, 1947. pg 18.
- "Modern Features Seen in Westberg Home Plan" Spokane Daily Chronicle, March 23, 1937.
- Rifkind, Carole. A Field Guide to Contemporary American Architecture. A Dutton Book. New York, NY, 1998. pg 270-277.
- The Blue Book of Home Plans for Home in the Pacific Northwest, Pacific First Federal Savings & Loan Association, Tacoma, 1937
- Universal Small Homes: Book 16. Universal Plan Service, Portland, OR. 1941.
- Universal Small Homes: Book 17. Universal Plan Service; Portland, OR. 1942
- Universal Small Homes: Book 21. Universal Plan Service, Portland, OR. 1950
- Universal Small Homes: Book 22. Universal Plan Service, Portland, OR. 1952.
- Petite Home of Budget Appeal - National Planning Service. c. 1939
- Whiffen, Marcus. American Architecture Since 1780: A Guide to the Styles. 4th ed. MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass. 1996.




